What’s up with… Telefónica Tech, ETSI, GSMA

By TelecomTV Staff
Apr 8, 2025
© Telefonica Tech
- Telefónica Tech eyes automated warehouse services
- ETSI unveils NFV architecture for 6G
- Mobile money accounts surpass 2 billion
In today’s industry news roundup: Telefónica Tech partners with robotics specialist Dexory to optimise warehouse management for real-time data analysis and automation; a new network functions architecture from ETSI builds on the current MANO framework to include support for future network generations; ‘mobile money’ hits 2 billion accounts milestone and boasts significant transaction growth, according to a new GSMA report; and much more!
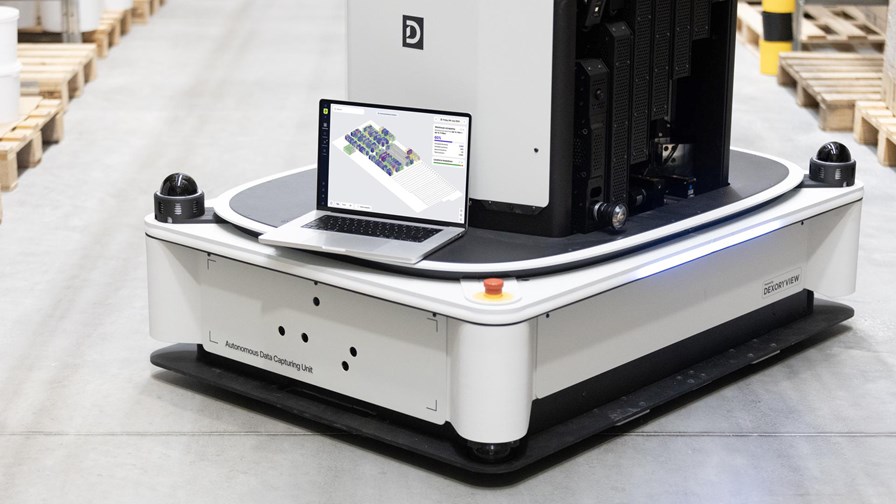
Telefónica’s digital business unit, Telefónica Tech, has formed an alliance with robotics and data intelligence company Dexory to promote automated warehouse management. The two companies will combine Telefónica Tech’s internet of things (IoT) connectivity and its integration capabilities with Dexory’s AI-powered digital twin platform DexoryView to help digitally transform the logistics sector. Telefónica Tech will also integrate this service with customers’ existing warehouse management systems to synchronise and manage all warehouse operations. “The alliance with Dexory allows us to strengthen our portfolio of digital services for the industrial sector, which plays a key role in the country’s competitiveness,” said Alfredo Serret, global director of IoT at Telefónica Tech. DexoryView uses fully autonomous robots to gather data from warehouses, through advanced optical cameras and LiDAR sensors, and is capable of scanning up to 10,000 locations per hour. The data is then analysed in real time and visualised on the DexoryView platform, using Telefónica Tech’s IoT connectivity, providing accurate information of the inventory as well as making suggestions on optimising the warehouse space.
ETSI has introduced a new network functions virtualisation (NFV) architecture that evolves the current MANO architecture towards an approach based on the concept of the telco cloud. The details are explained in a whitepaper entitled NFV evolution: Towards the Telco Cloud and an associated group report created by the ETSI NFV ISG to address the need for NFV to support emerging use cases and technological advancements anticipated in future network generations, particularly 6G. The approach builds on the requirements of network simplification, cloud nativeness, software portability across diverse infrastructures, sustainable evolution, enhanced automation, flexibility, modularity and scalability. “By embracing cloud-native principles, enhanced automation, and cutting-edge technologies like AI and digital twins, we are redefining NFV to meet the demands of next-generation networks, including 6G and virtualised RAN,” said Nakajima Yoshihiro, chair of ETSI NFV. “We strongly believe this evolutionary framework, underpinned by robust principles and forward-thinking enablers, will solidify NFV’s role as a cornerstone of the telecom industry’s digital transformation.” Other technological enablers explored in this work include declarative management APIs, GitOps methodologies, resource and service controller-based platforms, ‘data-as-code’ approaches and versatile data models, and the integration of big data, digital twins and AI. The group says its new proposed platform-oriented framework will help network operators leverage existing cloud infrastructure solutions and make telecom network deployments more reliable and sustainable
The GSMA has published its annual report, State of the Industry Report on Mobile Money 2025, into the mobile money sector and says that there are now over two billion registered accounts worldwide and over half a billion monthly active users. It calculates that approximately 108 billion transactions, totalling over $1.68tn, were processed through mobile money accounts in 2024. Year on year, transaction volumes increased by 20%, while transaction values grew by 16%, up from a 13% increase in 2023. As per the IMF’s definitions, ‘mobile money’ is a pay-as-you-go digital medium of exchange and store of value using mobile phones, facilitated by a network of mobile money agents. It is a financial service primarily offered to its clients by a mobile network operator or partner, independent of the traditional banking network. Unlike ‘mobile banking’, a bank account is not required to use mobile money services. The GSMA says that the industry took 18 years to achieve one billion registered accounts and only five years to reach two billion. It adds that in East Asia and the Pacific, many mobile money providers have evolved into full-service financial platforms, offering a broad range of products. Sub-Saharan Africa remains the world’s most active mobile money region, driven by new registered accounts and rising monthly activity in East and West Africa. However, Vivek Badrinath, GSMA director general, warns: “To ensure mobile money remains accessible, affordable, and safe, it is vital for governments and regulators to work with financial service providers to support financial literacy programmes, empowering underserved populations and opening new opportunities for financial decision-making.”
Vodafone has connected its 200 millionth internet of things (IoT) device. In the past five years, Vodafone says it has more than doubled the number of IoT connections in its network to over 200 million, more than a quarter of which are located in Germany. The device that achieved this milestone was, apparently, a healthcare monitor connected by Vodafone to its globally managed IoT network that provides doctors with information about a patient’s cardiac health and certain vital signs remotely. “This milestone is just the beginning of our hyperscale journey, and I’m sure we’ll be celebrating many more moments like this in years to come,” said Erik Brenneis, CEO of Vodafone IoT. Vodafone is also integrating its IoT SIM directly into a chipset of a device at the point of manufacture. The technique, known as iSIM, simplifies processes, reduces costs and automates deployment of the network service, making the technology particularly effective for large-scale IoT deployments, like smart labels used to track parcels through their journey. The first Vodafone IoT device was an in-car window-screen mounted navigation unit connected back in 2009.
UKTIN, the innovation network for the UK telecoms sector, has published a new report on the semiconductor industry and its application to telecoms. The report summarises semiconductor-related research, development and innovation (R&D&I) activities within the UK telecoms sector and offers a non-technical perspective on the current state of R&D&I efforts in this (increasingly geopolitically-sensitive) area. It also covers related technologies, such as photonics and radio-frequency engineering, and considers some overlapping domains beyond pure telecoms applications, such as military communications. The report notes that the rise of compound semiconductors like gallium nitride and indium phosphide offers promising alternatives to traditional silicon, particularly in niche applications requiring enhanced energy efficiency and performance. As the industry progresses towards smaller, faster and more efficient components, these emerging technologies and materials could well be crucial in overcoming the limitations of current technologies and support next-generation telecoms. “It’s important to recognise both the fundamental links between semiconductor research and advances in telecoms,” said Joe Gannicliffe, head of RF and photonics at CSA Catapult, one of the UKTIN delivery partners. “The UK has a real chance to build on advanced communication technologies if properly supported through skills development and targeted long-term R&D funding.”
Sustainable technology lifecycle solutions company TXO has expanded its presence in North America with the addition of network infrastructure products and services specialists the AirWay Group. Airway’s services include the supply of new and repurposed network equipment, certified recycling and asset recovery, network commissioning and decommissioning, and bespoke warehousing and logistics programmes. AirWay works with all four major US national carriers and the acquisition will increase TXO’s scale in the region. “We’re proud to join the TXO Group at a time when the industry is seeking smarter, cost-effective and more sustainable ways to manage network infrastructure,” said Tom Eaton, CEO of AirWay. The integration of AirWay expands TXO’s warehousing footprint and engineering services in North America, enhancing its ability to offer full lifecycle support – from staging and site kitting to equipment commissioning, asset decommissioning and agile sourcing. Simon Wort, group CEO of TXO, added: “Together, we will accelerate our impact and continue building a truly global circular economy.”
– The staff, TelecomTV
Email Newsletters
Sign up to receive TelecomTV's top news and videos, plus exclusive subscriber-only content direct to your inbox.
Subscribe