How SoftBank will deploy its large telco model (LTM).
- Telcos generate gargantuan volumes of data but have struggled to make best use of it
- Hopes have been raised in the past two years that generative AI platforms might harness the potential of telco data
- Now SoftBank and Tech Mahindra have developed customised large language models (LLMs) developed using telco data sources
- In addition, they, and others, are developing AI network agents to enable automation and improve telco productivity and efficiencies
In an effort to develop tech that might at last make better use of the massive volumes of network and operational data they have at their disposal, Japan’s SoftBank and India’s Tech Mahindra have developed so-called “large telco models” (LTMs) – customised, multimodal large language models (LLMs) trained specifically on telco network data – that can be used to introduce automated processes, improve productivity and enable operational efficiencies.
The LTMs have been developed using Nvidia NIM and NeMo microservices that are part of the AI technology giant’s AI Enterprise platform and were unveiled during the first full day of Nvidia’s GTC event being held in San Jose, California.
In addition to the customised, telco sector-specific LLMs, SoftBank and Tech Mahindra, as well as Amdocs, BubbleRAN and ServiceNow, are using LTMs to develop AI agents that, according to Nvidia, “automate complex decision-making workflows, improve operational efficiency, boost employee productivity and enhance network performance.” (In case you’d forgotten, we are now in the era of agentic AI…)
“Network data is special,” noted Nvidia’s head of telecom, Ronnie Vasishta, in a pre-GTC briefing. “Firstly, network data goes beyond text, video and images. It includes blogs, configs, MOPs [methods of procedure] and SOPs [standard operating procedures] and architecture diagrams, logical connectivity information and alarms. There’s a massive amount of unstructured data and continuous streaming of that data over any network… Large telco models are trained to understand the language of the networks. To leverage those large telco models, you need hundreds of AI agents all working together, which makes that scaling much faster,” he stated.
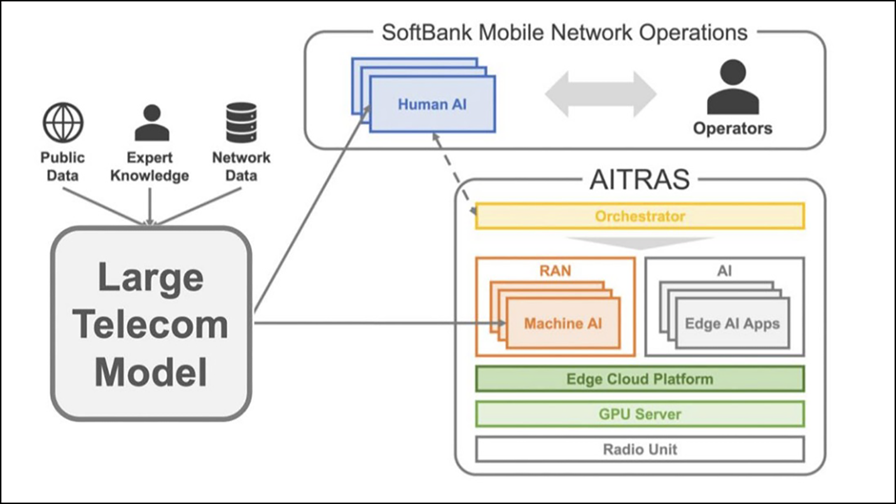
SoftBank’s LTM has been trained on “diverse datasets, ranging from SoftBank’s huge network data to the design, management, and operational know-how the company has accumulated over many years,” the Japanese operator noted. “The LTM enables advanced inference in the design, management, and operation of cellular networks,” noted the operator, adding that it has “also developed specialised AI models by fine-tuning the LTM, which is specifically designed to optimise base station configurations that enable advanced cellular network operations. The fine-tuned models were tasked with predicting configurations for actual base stations that had been excluded from the training phase, and their predictions were later verified by in-house experts to have over 90% accuracy. Compared to manual or partially automated workflows, the LTM-led approach reduces the time to make these changes from days to minutes, and with similar accuracy, indicating the potential for huge operational time and cost savings, in addition to reducing human error,” stated SoftBank.
“These results demonstrate that, by fine-tuning the LTM for specific use cases, it will become easier to develop dedicated AI models tailored to various operational scenarios in cellular networks,” the company added.
SoftBank aims to integrate various AI models based on the LTM with the orchestrator of AITRAS, the AI-RAN integrated solution being developed by the operator in partnership with Nvidia and others, which it unveiled in November last year. (See the diagram above.)
Tech Mahindra’s LTM has been used to develop the systems integrator’s Adaptive Network Insights Studio, which “provides a 360-degree view of network issues, generating automated reports at various levels of detail to inform and assist IT teams, network engineers and company executives,” noted Nvidia. “In addition, Tech Mahindra’s Proactive Network Anomaly Resolution Hub is powered by the LTM to automatically resolve a significant portion of its network events, lightening engineers’ workloads and enhancing their productivity,” it added.
The age of AI agents
The Amdocs Network Assurance Agent, developed using its amAIz platform, “automates repetitive tasks, such as fault prediction. It also conducts impact analysis and prevention methods for network issues, providing step-by-step guidance on resolving any problems that occur.” In addition, its Network Deployment Agent simplifies Open RAN adoption by automating integration and deployment tasks as well as interoperability testing.
BubbleRAN, meanwhile, is “developing an autonomous multi-agent RAN intelligence platform on a cloud-native infrastructure, where LTMs can observe the network state, configuration, availability and KPIs to facilitate monitoring and troubleshooting.” In addition, the platform “automates the process of network reconfiguration and policy enforcement through a high-level set of action tools” and taps into retrieval-augmented generation (RAG) pipelines and telco APIs to access real-time data.
And ServiceNow’s AI agents “drive productivity by generating resolution playbooks and predicting potential network disruptions before they occur,” as well as analysing network incidents and performing root cause analysis, according to Nvidia.
This is just the beginning – expect to hear a lot more about LTMs and telco AI agents during 2025.
- Ray Le Maistre, Editorial Director, TelecomTV
Email Newsletters
Sign up to receive TelecomTV's top news and videos, plus exclusive subscriber-only content direct to your inbox.
Subscribe